.NET Aspire, Microsoft's cloud-native stack, redefines how we approach distributed applications. With RabbitMQ & MassTransit, it's a powerful combination. Let's harness the potential of .NET Aspire, RabbitMQ & MassTransit to build resilient, cloud-native messaging architectures.
- Ensure you have:
- Latest .NET SDK
- Visual Studio 2022 Preview
- From Visual Studio Installer, install .NET Aspire SDK (Preview) by navigating to:
Modify -> Individual Components -> .NET Aspire SDK (Preview)
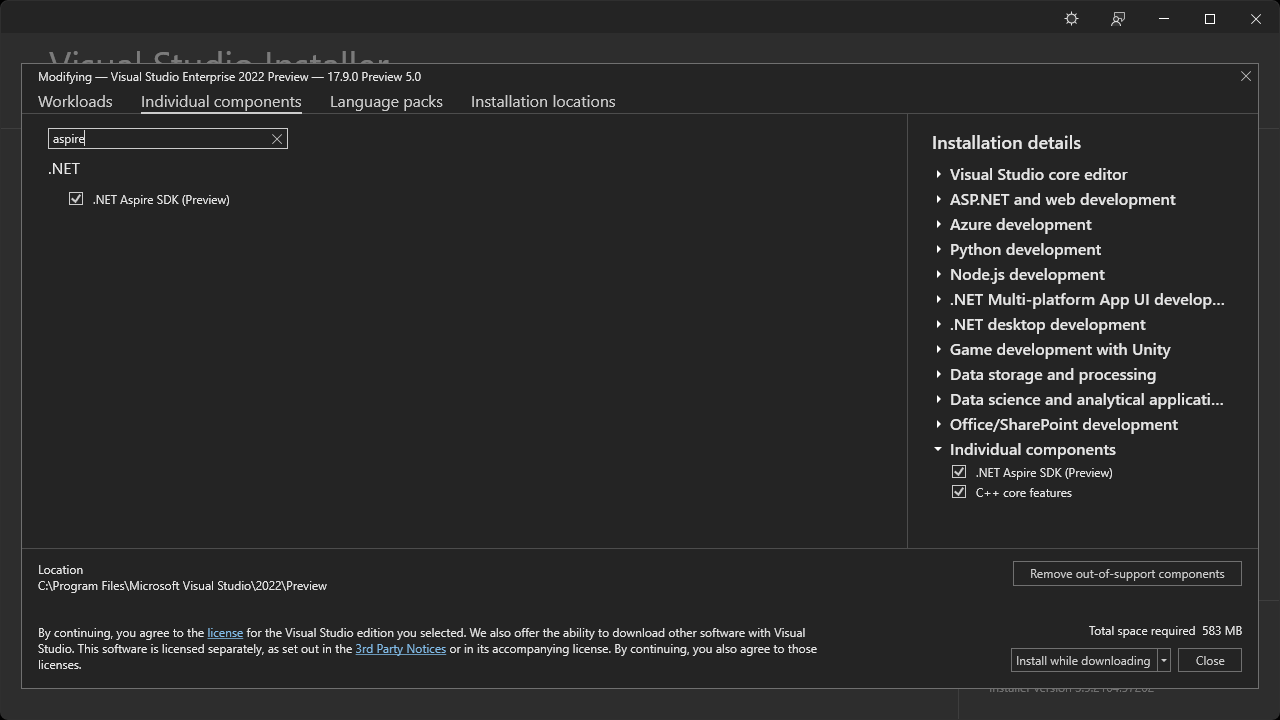
Update .NET Aspire Workload:
- Update the .NET Aspire workload via terminal with the following commands:
From a terminal, run the following commands to update the .NET Aspire workload,
dotnet workload update
dotnet workload install aspireCreate a New .NET Aspire Starter Application:
- Start with a fresh .NET Aspire Starter Application.
Update Existing Apps:
- For existing .NET Aspire apps, after installing the latest workload, update all .NET Aspire package references to:
9.0.0-preview.2.24162.2. If you prefer .NET 8, then update to8.0.0-preview.4.24156.9 - For example, update package references in the
AspireMessaging.AppHost.csprojfile forAspire.Hosting.
<PackageReference Include="Aspire.Hosting" Version="9.0.0-preview.2.24162.2" />Adding RabbitMQ Dependency:
- Add a RabbitMQ resource to the application. It bootstraps a container used for local development. Also add the resource reference to two other projects,
var messaging = builder.AddRabbitMQ("RabbitMQConnection");
var apiService = builder.AddProject<Projects.AspireMessaging_ApiService>("apiservice")
.WithReference(messaging);
builder.AddProject<Projects.AspireMessaging_Web>("webfrontend")
.WithReference(cache)
.WithReference(apiService)
.WithReference(messaging);- Your
appsettings.jsonfile should contain aRabbitMQConnectionproperty,
"ConnectionStrings": {
"RabbitMQConnection": "amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672"
}Message Contract Library:
- Add a new .NET Class Library e.g.
AspireMessaging.Contracts, which will contain the message contract classes. Add a simple record for messaging,
namespace AspireMessaging.Contracts
{
public record MessageContract
{
public Guid Id { get; init; } = Guid.NewGuid();
public DateTime CreationDate { get; init; } = DateTime.UtcNow;
public string Message { get; init; } = "";
}
}
- Add the class library as project dependency to
ApiServiceandWeb.
Installing MassTransit:
- Add the
MassTransit.RabbitMQpackage to bothApiServiceandWebusingNuget
<PackageReference Include="MassTransit.RabbitMQ" Version="8.1.3" />- Register
MassTransitservice in bothApiServiceandWebprojects,
builder.Services.AddMassTransit(x =>
{
x.SetKebabCaseEndpointNameFormatter();
x.UsingRabbitMq((context, cfg) =>
{
var configuration = context.GetRequiredService<IConfiguration>();
var host = configuration.GetConnectionString("RabbitMQConnection");
cfg.Host(host);
cfg.ConfigureEndpoints(context);
});
});The .NET Aspire RabbitMQ component supports Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration. It loads the RabbitMQClientSettings from configuration.Publishing Message:
- In the
_Imports.razorcomponent of theWebproject, add using statement forMassTransitand theAspireMessaging.Contractsproject references,
@using MassTransit
@using AspireMessaging.Contracts_Imports.razor- Replace content of the
Home.razorwith the following,
@page "/"
@rendermode InteractiveServer
@inject IBus Bus
<PageTitle>Home</PageTitle>
<button class="btn btn-primary mt-4" @onclick="DispatchMessage">Publish Hello, world!</button>
@code {
private async Task DispatchMessage()
{
await Bus.Publish(new MessageContract
{
Message = "Hello, world!"
});
}
}Consuming Message:
- In the
ApiServiceproject, add a class for consuming a message published using theMessageContractclass,
using AspireMessaging.Contracts;
using MassTransit;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AspireMessaging.ApiService
{
public class HelloWorldMessageConsumer : IConsumer<MessageContract>
{
public async Task Consume(ConsumeContext<MessageContract> context)
{
Debug.WriteLine($"Received: {context.Message.Message}");
await Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
}
- Register this consumer with
MassTransitservice,
builder.Services.AddMassTransit(x =>
{
x.SetKebabCaseEndpointNameFormatter();
x.AddConsumer<HelloWorldMessageConsumer>();
x.UsingRabbitMq((context, cfg) =>
{
var configuration = context.GetRequiredService<IConfiguration>();
var host = configuration.GetConnectionString("RabbitMQConnection");
cfg.Host(host);
cfg.ConfigureEndpoints(context);
});
});Test It Out Yourself:
- Download the repository from the link below,
https://github.com/fiyazbinhasan/AspireMessaging
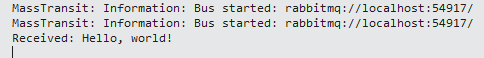
- Run the Aspire project and from the home page of the
Web, click on thePublish Hello, world!button, - In Visual Studio's
Outputpanel, you should see the debug message,


Comments